how to reduce aldehyde but not ketone Reactions of aldehydes and ketones — organic chemistry tutor
An aldehyde and a ketone are two different types of functional groups in organic chemistry. While they may seem similar, they have distinct differences in their structures and properties. Understanding these differences is crucial in various chemical reactions and the synthesis of different compounds.
Aldehyde
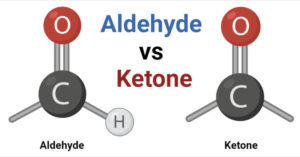 An aldehyde is a functional group that consists of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom (C=O) and a hydrogen atom (CHO). The general formula for aldehydes is RCHO, where R represents any alkyl or aryl group. This carbon-oxygen double bond gives aldehydes certain chemical and physical properties that differentiate them from ketones.
An aldehyde is a functional group that consists of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom (C=O) and a hydrogen atom (CHO). The general formula for aldehydes is RCHO, where R represents any alkyl or aryl group. This carbon-oxygen double bond gives aldehydes certain chemical and physical properties that differentiate them from ketones.
The presence of the hydrogen atom in aldehydes makes them more reactive than ketones. They undergo different reactions, such as oxidation, reduction, and nucleophilic addition reactions, due to the presence of an easily oxidizable hydrogen atom. Aldehydes also possess a characteristic odor, which is why certain aldehydes are commonly used in perfumes and fragrances.
Ketone
 A ketone is a functional group that consists of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom (C=O), with alkyl or aryl groups attached on both sides. The general formula for ketones is RCOR’, where R and R’ represent alkyl or aryl groups. Ketones have different chemical properties compared to aldehydes due to the absence of an easily oxidizable hydrogen atom.
A ketone is a functional group that consists of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom (C=O), with alkyl or aryl groups attached on both sides. The general formula for ketones is RCOR’, where R and R’ represent alkyl or aryl groups. Ketones have different chemical properties compared to aldehydes due to the absence of an easily oxidizable hydrogen atom.
Ketones are generally less reactive than aldehydes but still participate in various organic reactions. Common reactions involving ketones include nucleophilic additions, condensations, and reductions. Ketones are widely used in the pharmaceutical and chemical industries as intermediates in the synthesis of drugs, flavors, and fragrances.
Key Differences
To summarize the differences between aldehydes and ketones:
- Aldehydes have the general formula RCHO, while ketones have the general formula RCOR'.
- Aldehydes have an easily oxidizable hydrogen atom, while ketones do not.
- Aldehydes exhibit a characteristic odor, whereas ketones generally have a milder smell.
- Aldehydes are more reactive than ketones due to the presence of the easily oxidizable hydrogen atom.
- Ketones are commonly used as intermediates in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, flavors, and fragrances.
Understanding the differences between aldehydes and ketones is essential in organic chemistry. It allows chemists to predict and control reactions, design new compounds, and synthesize complex molecules for various applications. Whether it is determining reaction mechanisms or developing new drugs, a deep understanding of these functional groups is crucial for professional chemists.
If you are searching about Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones — Organic Chemistry Tutor you’ve visit to the right page. We have 5 Images about Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones — Organic Chemistry Tutor like LiAlH4 Reduction of Ketone and Aldehyde - the Mechanism | Chemistry, Aldehyde vs Ketone- Definition, 14 Key Differences, Examples and also Aldehyde vs Ketone- Definition, 14 Key Differences, Examples. Read more:
Reactions Of Aldehydes And Ketones — Organic Chemistry Tutor
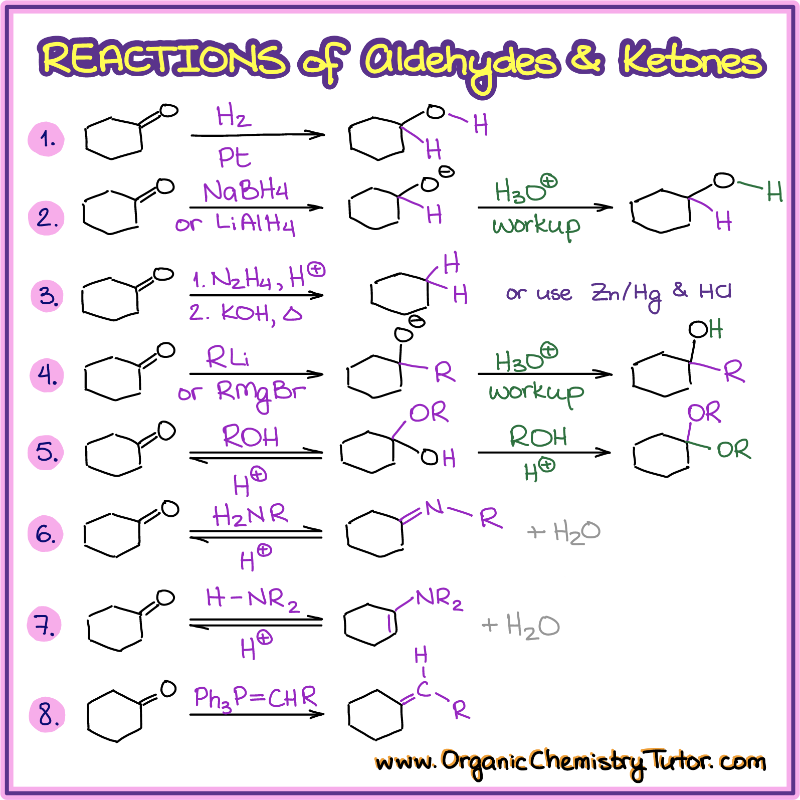 www.organicchemistrytutor.comaldehydes ketones organicchemistrytutor tutor aldehyde reduction
www.organicchemistrytutor.comaldehydes ketones organicchemistrytutor tutor aldehyde reduction
One Part Of Chemistry: Reactions Of Aldehydes, Ketones And Phenols
 1chemistry.blogspot.co.ukketones aldehydes test reactions fehling reagent brady solution chemistry part formation result
1chemistry.blogspot.co.ukketones aldehydes test reactions fehling reagent brady solution chemistry part formation result
Aldehyde Vs Ketone- Definition, 14 Key Differences, Examples
 thechemistrynotes.comketone aldehyde definition biorender
thechemistrynotes.comketone aldehyde definition biorender
LiAlH4 Reduction Of Ketone And Aldehyde - The Mechanism | Chemistry
 www.pinterest.co.uklialh4 reduction carbonyl nabh4 ketone aldehyde alcohols borohydride ketones carboxylic hydride addition citric ester sodium chemistrysteps reduktion oxidation mechanismus hydrogen
www.pinterest.co.uklialh4 reduction carbonyl nabh4 ketone aldehyde alcohols borohydride ketones carboxylic hydride addition citric ester sodium chemistrysteps reduktion oxidation mechanismus hydrogen
Introduction Aldehyde And Ketone - YouTube
 www.youtube.comReactions of aldehydes and ketones — organic chemistry tutor. Lialh4 reduction of ketone and aldehyde. Aldehyde vs ketone- definition, 14 key differences, examples
www.youtube.comReactions of aldehydes and ketones — organic chemistry tutor. Lialh4 reduction of ketone and aldehyde. Aldehyde vs ketone- definition, 14 key differences, examples